Kleiber's law and its possible implications for obesity
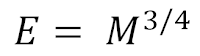
Kleiber's law ( ) is one of those “laws” of nature that is both derived from, and seems to fit quite well with, empirical data. It applies to most animals, including humans. The law is roughly summarized through the equation below, where E = energy expenditure at rest per day, and M = body weight in kilograms. Because of various assumptions made in the original formulation of the law, the values of E do not translate very well to calories as measured today. What is important is the exponent, and what it means in terms of relative increases in weight. Since the exponent in the equation is 3/4, which is lower than 1, the law essentially states that as body weight increases animals become more efficient from an energy expenditure perspective . For example, the energy expenditure at rest of an elephant, per unit of body weight, is significantly lower than that of a mouse. The difference in weight does not have to be as large as that between an elephant and a mouse for a clear differ...



